Subject of study: Transport network and its parameters
Goalofstudy:Improvement of traffic management system
Methodofstudy:Analyticalmethod
Theresultsthatwereattained: Proposal to construct a road (arcs 2-11,11-2), arrangement of traffic signal control at crossroads
Implementation recommendations: The project can be applied to the city under review.
Application field: Transport
TRANSPORT NETWORK, ROAD ACCIDENTS, ROAD CONDITIONS, TRANSPORT STREAMS, MAIN ROAD, TRAFFIC INTENSITY, LOADING LEVEL, ACCIDENCE RATE
Transport is one of the most important and largest branches of public production, extensive sphere of application of human labor and consumption of material resources. Fields of industry, civil engineering, agriculture, trade could not operate properly without large-scale transport servicing.
Anextensiverangeoftransportinfluenceoneverysphereofhumanactivitiesandsocialdevelopmentingeneraladvancesmulti-aspectdemandsfornormaloperationoftraffic (T), representingacomplexdynamic systemofinteractionoftransportandpedestrianstreams, acombinationofitsfourcomponents: driver – motor vehicle – road – environment (DMRE). The safety of T depends on reliability of the DMRE system components. Thus, the high level of road loading with traffic is a result of disproportion between the growing stock of vehicles and the network of motor roads. The high accident rate related to human factor is the result of disproportion between training levels and transport culture displayed by people involved in the traffic process.
The growing intensity, changes in the transport stream structure and speed conditions set more and more stringent requirements as to the methods of traffic management and control (TMC) to provide for an adequate traffic effectiveness and safety level, with the specified volume of carriage being guaranteed.
The T specifics is based on interaction of technical and human factors, which are rather difficult to manage due to the fact that millions of people are involved in the system of traffic, each of them having individual psycho- physiological properties, skills, experience, knowledge. A driver is affected by a range of negative factors: considerable volume of information to be continuously analyzed, chronic time deficit, high level of responsibility for all decisions being made. All those factors complicate the process of development of TMC measures. The ultimate goal of TMC is to secure effectiveness and safety of traffic.
The aim of this graduation project is the development and improvement of all conventional measures taken in respect of TMC. The analysis of TMC methods will be based on the specific example of a street network (SN). In addition, there will be identified traffic management (TM) disadvantages under given city conditions and developed essential measures to improve the TM system applied to given SN.
Chapter 1
PRIOR ART
1.1 Analysis of Methods for Improvement of Traffic Management System
To assure effective and safe operation of the DMRE system, one should be expected to improve the drivers’ training level, advance the structure and technical condition of transport facilities, extend street and road construction, provide for the optimum management of the traffic process.
The traffic management process involves the development of engineering and organizational measures to be taken to provide proper conditions for high-speed, safe and convenient transport and passenger traffic within the existing network of streets. Although the precise identification of this sphere is rather difficult, the engineering work on traffic management can normally be represented in the form of five general sets of factors.
– Analysis of traffic and generation of data on its management conditions. The development of traffic management measures is based on the information about the current traffic management conditions, data on intensity, structure of transport and passenger streams, as well as other traffic information. As a rule, such information is collected by an agency (engineering, road construction or maintenance, utility companies) entrusted with the task to work out a set of measures to improve the system of traffic management. The information is accumulated in the process of regular assessment of street network and traffic conditions.
– Investigation of road conditions, identification of zones of concentration of road accidents and “critical points” within the network of streets. The work on identification of zones of concentration of road accidents in the street network, places of limited traffic capacity, sectors where considerable deceleration of transport and passenger streams is observed is based on statistical data on road accidents, reports made out by the Motor Vehicles and Traffic Control Departments with the reference to violation of traffic regulations, assessment of traffic capacity of separate street network components, results of traffic condition analyses conducted with the use of mobile laboratories. As far as identification of unsafe zones is concerned, the above work must be regularly carried out by the Motor Vehicles and Traffic Control departments that service a particular city area, road. Assessment of “critical” points and traffic capacity can be made by both personnel of Motor Vehicles and Traffic Control Departments and agencies entrusted with the task to prepare traffic improvement proposals (projects).
– Engineering and economic justification of measures focused on traffic system improvement. Basing on the information about street network conditions, traffic management, road accidents and zones of their concentration, “critical” points, the traffic management projects (TMP) are developed, the adequate economic substantiation being provided. Depending on the task to be fulfilled, the project can be applied to a local road length (crossroads, street section) or a city (city area), motor road or municipal main road in general. Project engineers may only be represented by specialized engineering companies. The appropriate assignments must be devised by appropriate local administration departments with the participation of the Motor Vehicles and Traffic Control departments.
– Participation in implementation of measures to improve traffic management conditions. Personal involvement in the process of implementation of traffic management improvement measures in the form of field supervision allows to correct, if and when necessary, design decisions and, at the same time, verify them under practical conditions.
– Operational changes introduced to the system of traffic management in road accident zones, under conditions of traffic congestion and mass events. The operational traffic management changes to be made at the time of mass events (meetings, demonstrations, sporting events, festive corteges), as well as in cases of traffic congestion (exhaustion of traffic capacity) in certain parts of the street network, in road accident points, in the course of emergency rescue operations. The work on introduction of such operational changes is entrusted to Motor Vehicles and Traffic Control departments servicing a particular territory.
Usedforthetrafficinvestigationpurposesisagreatnumberofdifferentmethods, rangingfromthesimplestsingle-manmethodstothemostcomprehensivetechniques calling for the application of advanced electronic equipment and mobile laboratories. The process of traffic research is facilitated by the methods, involving the use of traffic automated control systems (TACS). The documentary, full-scale methods for modeling the processes of assessment of traffic characteristics and conditions are among the most applicable methods.
TheresearchandpracticalengineeringworkcarriedoutintheTMfieldhasallowedtodevelopasetofspecificengineeringdecisions, enabling to attain the desired results under conditions of mass traffic of transport facilities and passengers.
Consequently, the following TM improvement measures can be singled out:
– construction of multilevel intersections, which can be applicable to high-intensity interurban communication main roads, for the purpose of maintenance of high-speed conditions, as well as under conditions of high traffic concentration in municipal intersection points in those cases where signal control systems are not effective;
– prohibition of transport stops; this measure is to be applicable to the places where stationary transport facilities may course emergency situations, for example, in narrow, high-intensity streets;
– stream distribution in space and time; this method can be applied at crossroads to separate highly intensive streams of conflicting directions with the use of separate traffic phases and traffic lane differentiation methods;
– traffic lane differentiation for cars and trucks; this measure is to be taken to enhance the road traffic capacity in those cases where a share of motor trucks is large enough;
– arrangement of additional traffic lanes in high-concentration zones;
– operational traffic speed control, depending on visibility and road surface conditions; that is, installation of appropriate road signs warning about traffic condition and limiting speed;
– introduction of binding traffic control at crossroads; this method is applied to high-intensity intersection points or in the event of high accident rate at crossroads;
– establishment of a special service department for operational evacuation of faulty technical facilities, following road accidents;
– rational distribution of carriage types during the period of 24 hours; if possible, transfer of cargo traffic to night time not to create obstacles for car and route traffic;
– prohibition of traffic for certain types of transport facilities in main street areas, for example, in areas where motor trucks create considerable traffic jams;
– traffic speed limitation; the method is applicable to road lengths ofhigh accident rate;
– creation of no-transport zones; this measure can be applied to zones of high-intensity pedestrian communication: in parks, squares, etc.;
– differentiationof direction-oriented main roads;
– prohibition of left- and right-turn maneuvers, U-turns, overtaking; the method is applied under conditions of high intensity of relevant streams to reduce the risk of road accidents;
– arrangement of turns and U-turns outside crossroads zones;
– rational arrangement and separation in space of cargo- and passenger-generating facilities; dedication of extra traffic lanes for cargo and passenger transport under conditions of their high intensity, to reduce the rate of traffic congestion;
– arrangement of one-way traffic; the measure taken to abolish “network narrow zones”;
– assurance of high road grip coefficient as measure to enhance traffic safety, reduce risks of emergency situations;
– expulsion of transit traffic from general urban streams to lower traffic intensity on city main roadsand promote transit stream high-speed conditions;
– introduction of channeled traffic (compulsory distribution of transport streams between traffic directions);
– installation of road information boards, providing for timely and important data for people involved in traffic; installation of road signs to describe current traffic conditions (sharp corner, repair operations, etc.);
– assignment of special lanes for passenger transport;
– “specialization” of lanes at the entrance to crossroads, beginning from the point of indication of further traffic direction; this measure is taken to improve traffic capacity at crossroads.
The graduation paper project will further give consideration to a specific transport network. There will be identified all traffic network characteristics and disadvantageous features, including further assessment of a range of measures to be taken to improve the system of traffic within the arcs of the network under review.
1.2 Description of Subject of Study
The uniform street network (SN) represents a system of city streets and roads. The assessment of ST development is based on the length and density of the network of streets. STs may have a different density, which represents a ratio of the total length of streets and roads in kilometers to a given area in square kilometers.
The main components of a motor road and whole SN, which have an impact on the traffic effectiveness and safety level are as follows: line pattern, road vertical alignment and cross-section, slopes, curvature in plan and profile, road surface type and condition.
Motor road intersection points create transport junctions. A combination of roads and transport junctions forms a planning (geometrical) structure of the municipal network of streets.
1.2.1 Transport Network Pattern
The major disadvantage of the existing transport network in the area is caused by the fact that its planning parameters do not meet the present-day municipal traffic requirements: the adequate traffic capacity in transport junctions provided with single-level intersection points is limited, traffic speed is low, adequate safety of transport and passenger traffic is not provided.
The standard disadvantageous aspects of the planning structure and transport servicing system are as follows:
– noclear separation between streams of cargo and passenger traffic;
– nonconformity of streets (in respect of their class) with the main parameters of the existing transport main roads;
– improper connection between local city and interurban transport;
– inadequate consideration of traffic safety requirements in respect of transport and passengers.
The pattern of transport network in the area is presented in the form of a layout chart. The graph nodes shown in the chart represent transport junctions that “absorb” and “generate” transport streams, while the edges designate the sections of streets, interconnecting the nodes. Figure 1.1 below shows the graphic representation of the chart.
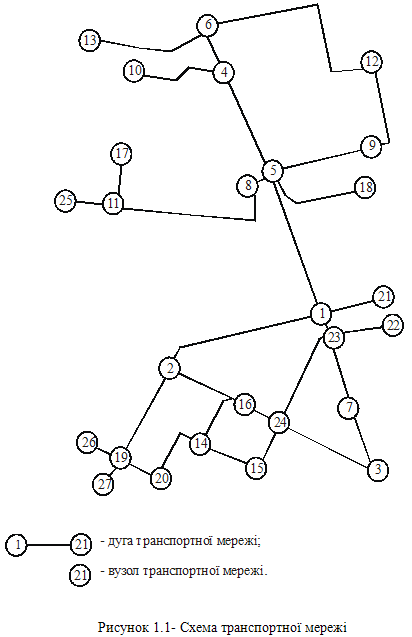
Figure 1.1 Transport Network Layout Chart
Transport network arc
Transport network junction
1.2.2 Analysis of Road Accidents
Assurance of safe transport and passenger traffic in streets and roads presents an important and complex problem. The rapidly growing quantity of transport facilities, dramatic intensification of traffic give rise to much more frequent road accidents of a higher degree of severity, causing death and injury of people, material loss resulting from damage caused to transport facilities, cargoes, installations, etc. The analyses and development of accident prevention measures are based on detail road accident reports classified according to the prescribed forms [2,4,7].
To analyze a road accident, both quantitative and qualitative aspects of the event should be assessed. Parameters of classification of accidents, basing on causes of their occurrence,allow to define the accidence and traumatism prevention measures, while the purely quantitative type-wise analysis of accidents does not provide adequate grounds for it. The quantitative analysis of statistical data permits to make percentage distribution of road accidents, depending on their causes [3,5,7]..
To identify unsafe zones of concentration of road accidents and their main reasons, it is found advisable and reasonable that each accident be assigned a conventional designation on the map. Such conventional symbols must be marked on the map during the whole year. When compiling the annual maps, the changes in a number of accidents in streets during the period of several years can be assessed. By comparing the annual maps, one can also trace some trends or concentrations as regards the accident rate reduction, following implementation of certain measures.
Table 1.1 belowshows distribution of road accidents in zones of their concentrations over the period of one year.
Table1.1StatisticalData on Road Accidents
|
Zones of road accident concentration (Crossroads No.) |
Total number of accidents |
Number of victims |
|
|
Killed |
Injured |
||
|
5 |
1 |
– |
0 |
|
23 |
4 |
– |
3 |
|
6 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
11 |
2 |
– |
2 |
|
2 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
1.2.3 Road Conditions
At the current time of rapidly growing municipal motor rolling stock and intensive saturation of cities and towns with motor transport, higher speeds and improved dynamic properties of motor vehicles, the requirements to road conditions should become more stringent. In the aggregate, the above requirements must ensure safety and comfort of transport traffic in the course of carriage of cargoes and passengers, adequate speed and efficiency. Among the most important components of road conditions are the road surface quality, width of passage part, width and quantity of traffic lanes, road visibility, provision of people involved in traffic with essential information, adequate lighting [1,3].
It was found in the course of the analysis that all important roads in the area have asphalt-concrete surfaces, except for the roads passing through the private sector. However, they do not have any practical influence on the network in general.
Inthecourseoffull-scale investigation there were studied the following road condition characteristics essential for the project fulfillment purposes: quantity of traffic lanes, free traffic speed, length of network arcs, width of lanes.
1.2.4 Transport Stream Characteristics
To solve the traffic-related problems, the following data must be obtained:
– data on intensity of transport and passenger traffic;
– data on transport traffic speed in different street sections;
– dataontransportstreamcomponents.
Tables 1.3 – 1.4.[ 5,7] presenttheactualdataontransportstreamcharacteristicsinrespectofjunctions (transportdemand) andarcs (intensityoftransportstreams) ofthetransportnetwork.
1.2.5 Characteristics of Performance of Technical Control Facilities
As far as traffic management is concerned, the problem of transport stream control becomes the most critical one under conditions of a rapid growth of the motorization level. Introduction of adequate technical facilities is one of the most important traffic management measures. As concerns their purpose, the traffic management technical facilities can be subdivided into the following major groups:
– technical facilities that have a direct effect on transport and pedestrian streams for the purpose of generation of their proper parameters; relating to such facilities are the road signs, road marking, traffic lights, and guides;
– technicalfacilitiesprovidingforadequateoperation of the first-group facilities according to prescribed algorithms; they are road controllers, transport detectors, data processing and transmission facilities, equipment for TACS control stations, dispatch communication facilities, etc. [1,2,4].
1.3 Conclusions to Chapter
Chapter 1 was addressed to the analysis of SN technical and transport characteristics. Subject to analyses were the data on the length and quality of road surfaces in some network zones, intensity and speed of transport streams in network arcs. The chapter was also focused on the analysis of transport accidents within the network, which allowed to identify the points of the maximum concentration of road accidents. Using all the data that have been collected, the graduation paper project will further concentrate on the development of methods to be adopted with a view to improving the TM system in this particular network and reducing the risk of road accidents in the points of their concentration.
Chapter 2. Traffic Network Management
Chapter 2 gives consideration to the development of the transport network performance model, analysis of the network operation parameters, network parameter variations.
Chapter 3.Introduction of System of Traffic Lights Control at Crossroads
Chapter 3 is addressed to the assessment of traffic intensity in different route directions, selection of a phase-wise turnout patterns, calculation of traffic-lights cycle parameters, evaluation of traffic delays, estimation of a degree of complexity and hazards at crossroads.
Chapter 4.Assessment of Effectiveness of Project Solutions
Discussed in Chapter 4 are the economic, social and ecological parameters.